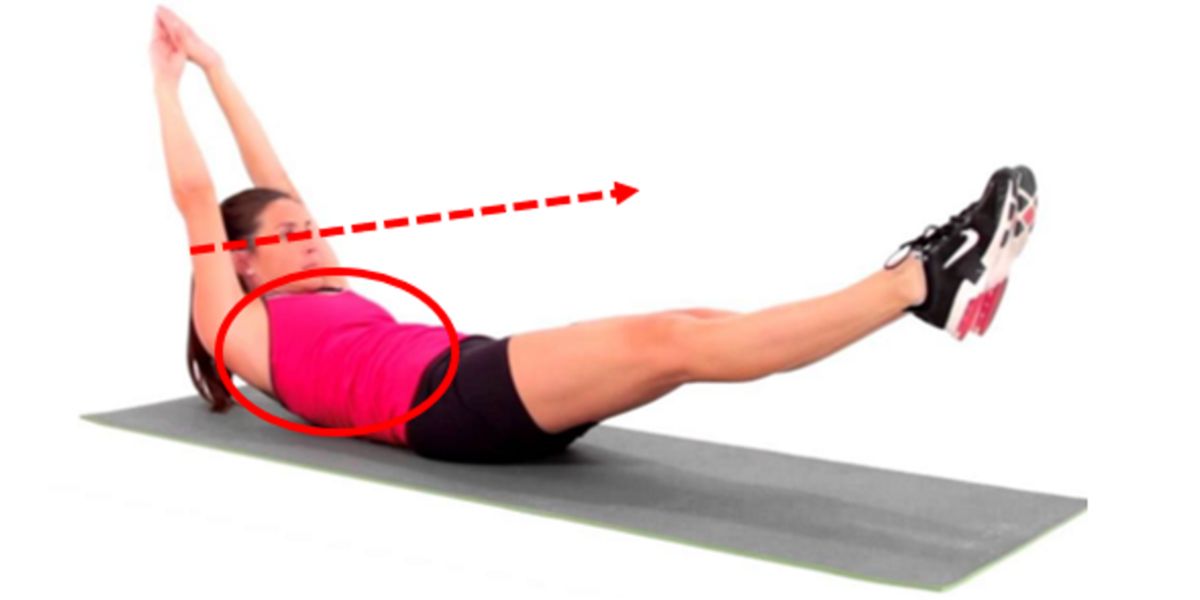
Hollow Body Hold is a difficult exercise for some people and easy for others. The goal is to be able to maintain a stable position for a long time.
Challenge your body
Few people experience many difficulties when a neutral standing position is maintained or even when the vertical position is varied.
However, it is necessary to understand and advance the range of motion of the human body , responding better under a stressor or stimulus, challenging the neutral position of the spine by introducing simple requests for controlled movements.
Gravity affects the positioning of the spine in space, therefore, change the position relative to the ground, such as lying face up on the back, would add a controlled challenge.
A simple assessment of all the global anterior musculature that is responsible for d and maintaining the Hollow position, would be to perform the exercise and observe how the amount of muscle tension required decreases and how the shape of the exercise is lost, increasing tremors and reducing the position (Flinch).
What is Hollow-Body-Hold
Hollow Body Hold is a basic overall exercise , isometric type, oriented towards the lumbo-abdominal complex (Core) and with great transfer potential to physical activity, physical and sports exercise, for example, sports gymnastics, crossfit, rhythmic gymnastics, swimming …
Benefits
This fantastic exercise is characterized by:
- High transfer towards other sports and health-oriented physical activity.
- Need for motor control .
- Activation of the global muscle .
- Adaptability and personalization in different profiles of people.
- Analytical muscle activation : anterior serratus (protraction of the shoulder) , tight posterior (breathing) and gluteal muscles (pelvic retroversion).
Build your Hollow Body Hold
Stretch as much as possible
Both ends of the body should be stretched to the maximum, as part of their aesthetic expression, creating tension and generating movement.
Consequently, if the feet / toes ( “Pointed Toes” ) and arms are in extension, they will produce tension that will be transmitted from one end to the other, as if it were a cable.
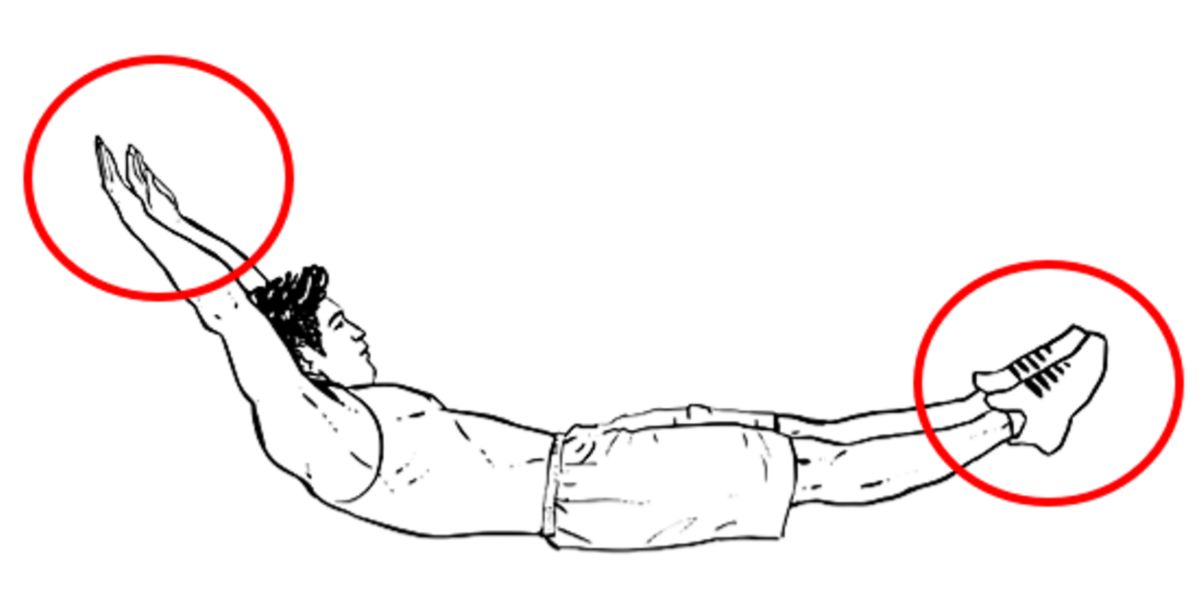
There are various reasons from the structural and anatomical point of view, but in terms of motion control, it is because the stretching of the nervous system creates more tension in the body and allows a great application of forces.
Pelvic retroversion
In short, retroversion pelvic occurs when the pelvis is moved backward as a result of pulling the hamstrings and glutes.
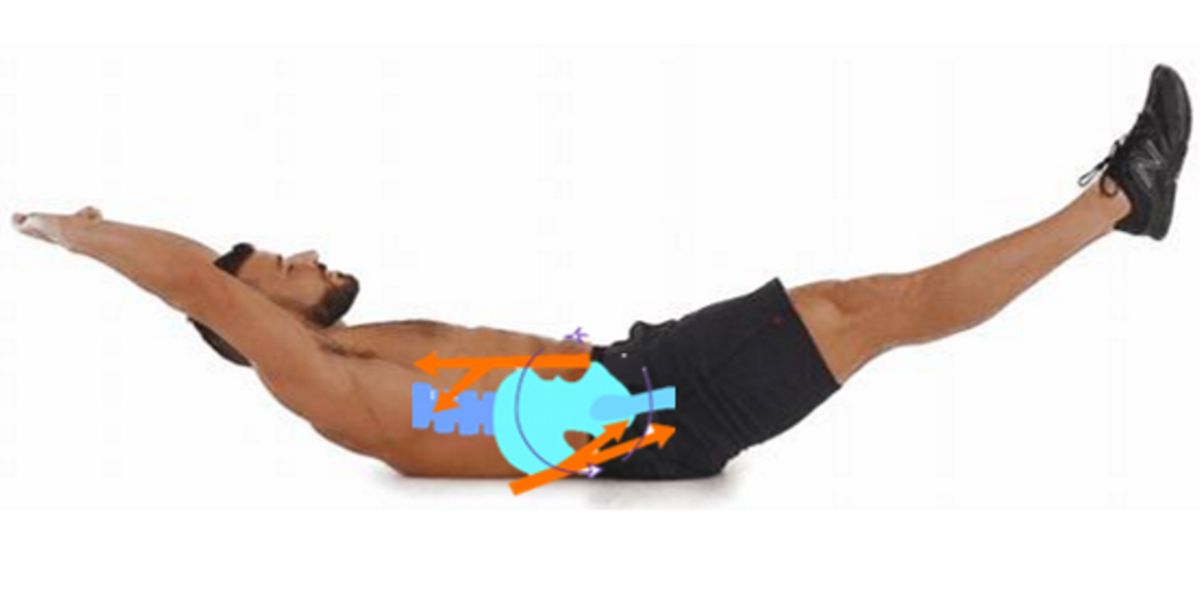
Conversely, the ‘ pelvic anteversion occurs when the pelvis moves forward (lumbar arch position).
Specifically, exaggerating these two positions will cause problems as it will cause the lumbar arch to be too pronounced (in the case of anteversion) or to completely lose retroversion.
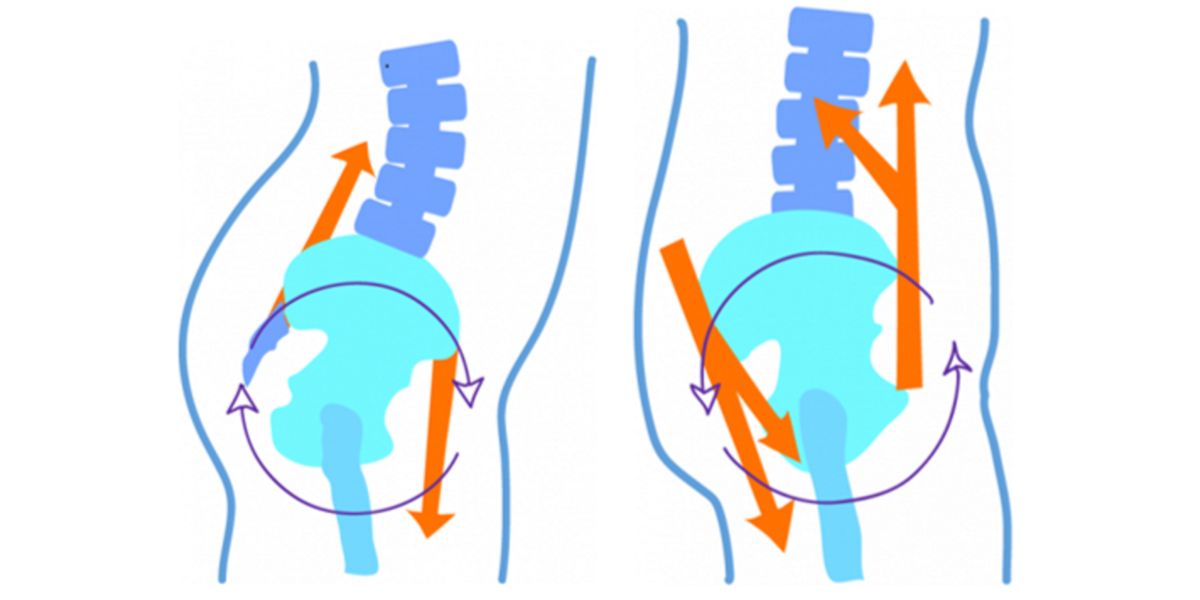
Achieving pelvic retroversion is in some cases a complex and difficult task to understand.
So, a task of teaching and body awareness would be to put the subject upright and make him think he has a screw between the buttocks, the idea is to prevent that screw from falling and to orient it downwards, generating a downward tilt of the pelvis , together with the activation of the gluteal muscles, therefore, pelvic retroversion.
Activates the Serrati
Serrato anterior
The Serrato Anterior is a muscle located on the lateral side of the thorax, originating from the anterior aspect of the vertebral edge of the scapula, to insert on the anterolateral aspects of the first 10 ribs.
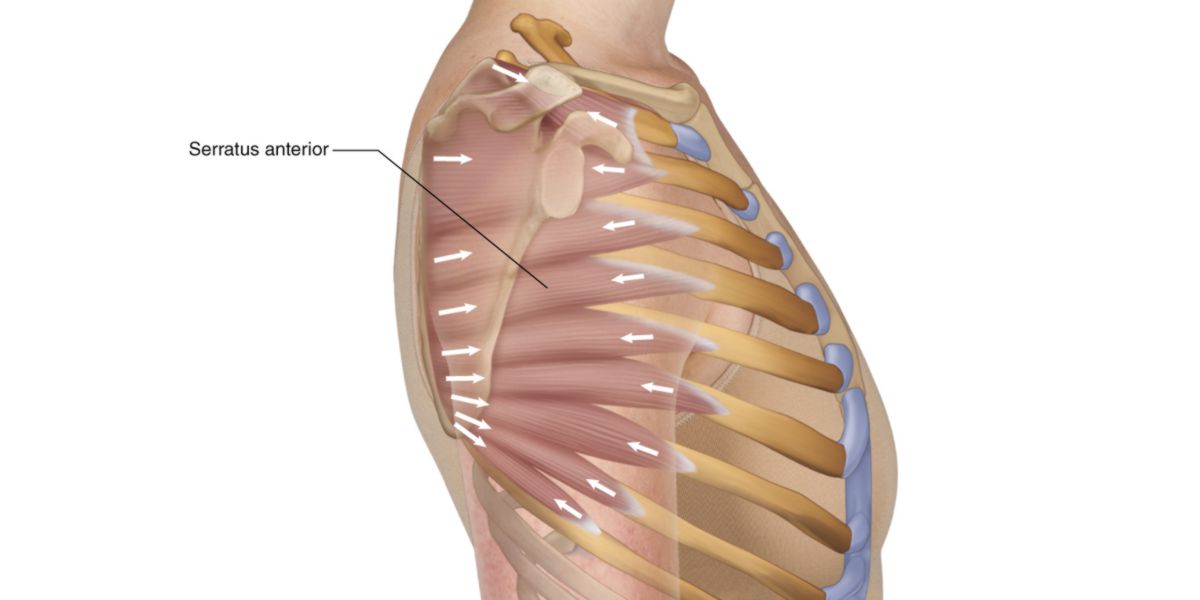
Its main function is to control the movements of the shoulder blade.
Consequently, the activation of this muscle would radiate tension towards the central area and, together with pelvic retroversion, would increase the level of muscle activation.
Serrato posterior
D ‘ on the other hand, the Serrato Posterior Superiore , located in the upper part of the back (extending from the spine to the first ribs) is a muscle responsible for lifting the first ribs, being a stimulating musculature.
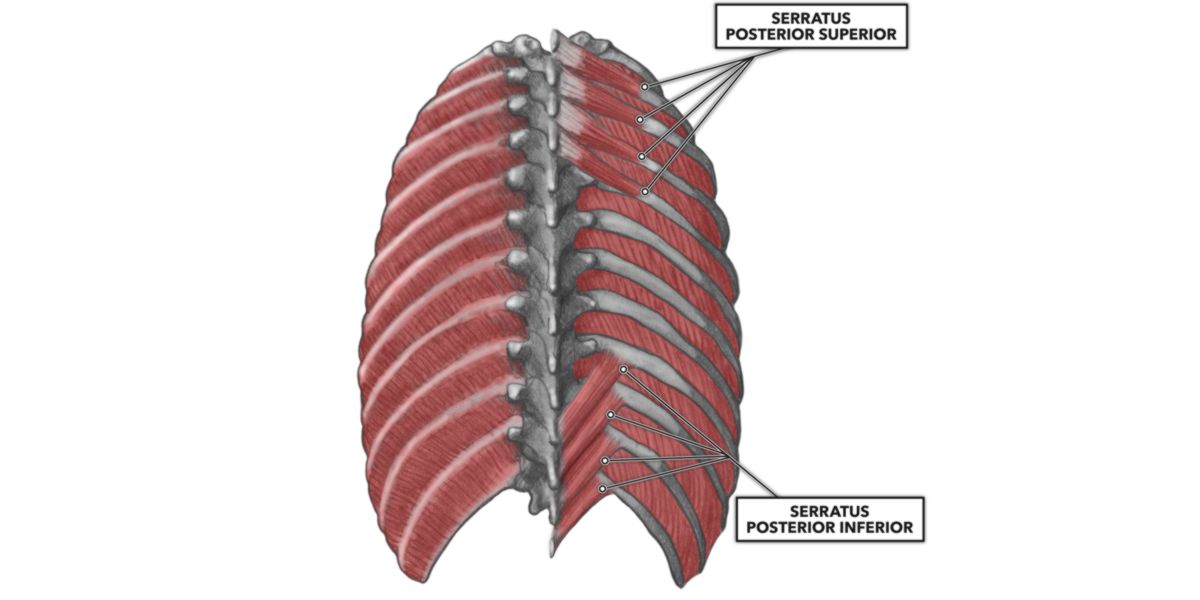
In relation to it, the Serrato Posterior Inferior , located in the lower back (from the spine to the last four ribs) , on the contrary, it is an expiratory muscle.
However, it plays an important role with large dorsal and superior posterior serratus in protecting and compacting the ribs.
In summary, recommendations to be developed in relation to the muscles forming the serratus would be the following:
- Scapular protraction.
- Shoulders flexed by 180º.
- Ribs in.
- Control the respiratory cycle.
Tighten the abdomen
Extension of the upper and lower limbs through thoracic flexion, shoulder flexion and protraction, and knee and foot extension elevates the spinal load by creating muscle tension around the abdomen , but it does not generate stress in the lumbar spine if the movement is individualized and performed correctly.
The increase in tension ne The lumbar vertebrae require a compensatory increase in tension in the abdomen to maintain a neutral position.
Lower Back
The Hollow Body Position is a great exercise to learn how to load the lower back (lumbar spine), which is very sensitive to extension and jerk (narrowing or setbacks in position after muscle fatigue or loss of motor control).
Tremors
The tremor that can be observed in the Hollow Hold position expresses a series of micro-flinches , which reflect the loss of physiological motor control.
The 5 points fundamental to achieve Hollow Body Hold
- Adapt the exercise according to the level and needs.
- Create effective and efficient levers: “Stretch as much as possible”.
- 180º shoulder flexion .
- Extension of the knees, feet and toes.
- Legs always together.
- The arms will be at shoulder height.
- Protect the lumbar spine and improve muscle activation: “Retroversion pelvic “.
- Secure and keep the lumbar / pelvic area in contact with the floor.
- Activates the gluteal muscles.
- Activates the upper limb and emits tension towards the central area: “ Activation of Serrati ”.
- Scapular protraction.
- Ribs in.
- Costal breathing.
- Optimize the position of the Hollow: “stretch the abdomen ”.
- Chest flexion.
- Slight flexion of the neck.
How to reach Hollow-Body-Hold? Progression
Finally, we present a basic progression of the exercises that will help any subject to correctly develop the pre-requisites necessary to reach the last position the Hollow Hold .
Tuck Hollow (grouping)
| Training load | |||
| Time of Work | 5-20 ″ | Series | 2-4 |
| Intensity | 3/10 | Rest | 20-40″ |
Tuck Hollow (pushing the knees )
| Training Load | |||
| Work Time | 5-20 ″ | Series | 2-4 |
| Intensity | 4/10 | Rest | 20-40 ″ |
Tuck Hollow (arms outstretched)
* Without oscillations.
| Training load | |||
| Working Time | 5-20 ″ | Series | 2-4 |
| Intensity | 5/10 | Rest | 20-40 ″ |
Middle Tuck Hollow (arms extended and knees bent)
5-20 ″
| Training Load | |||
| Working Time | Series | 2-4 | |
| Intensity | 3/10 | Rest | 20-40 ″ |
Hollow (knees extended and arms bent)
| Training Load | |||
| Work Time | 5-20 ″ | Series | 2-4 |
| Intensity | 4/10 | Rest | 20-40 ″ |






